The Emergence of AI in Healthcare: What It Means for Emergency Medicine

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the healthcare industry as a whole, and in emergency medicine, in particular, its influence is immense. Emergency departments (EDs) tend to be high-stress & very fast-paced environments. AI technologies integrated into these environments are real game-changers, allowing for quicker, more precise diagnoses and more streamlined workflows.
From triage to treatment planning, and from real-time monitoring to documentation, AI is being deployed to increase the speed, safety, and accuracy of emergency care. This article covers how AI is revolutionizing emergency medicine, featuring real-world examples, technological developments, expert opinions, and challenges associated with adoption.
The Evolution of Emergency Medicine and the Rise of AI
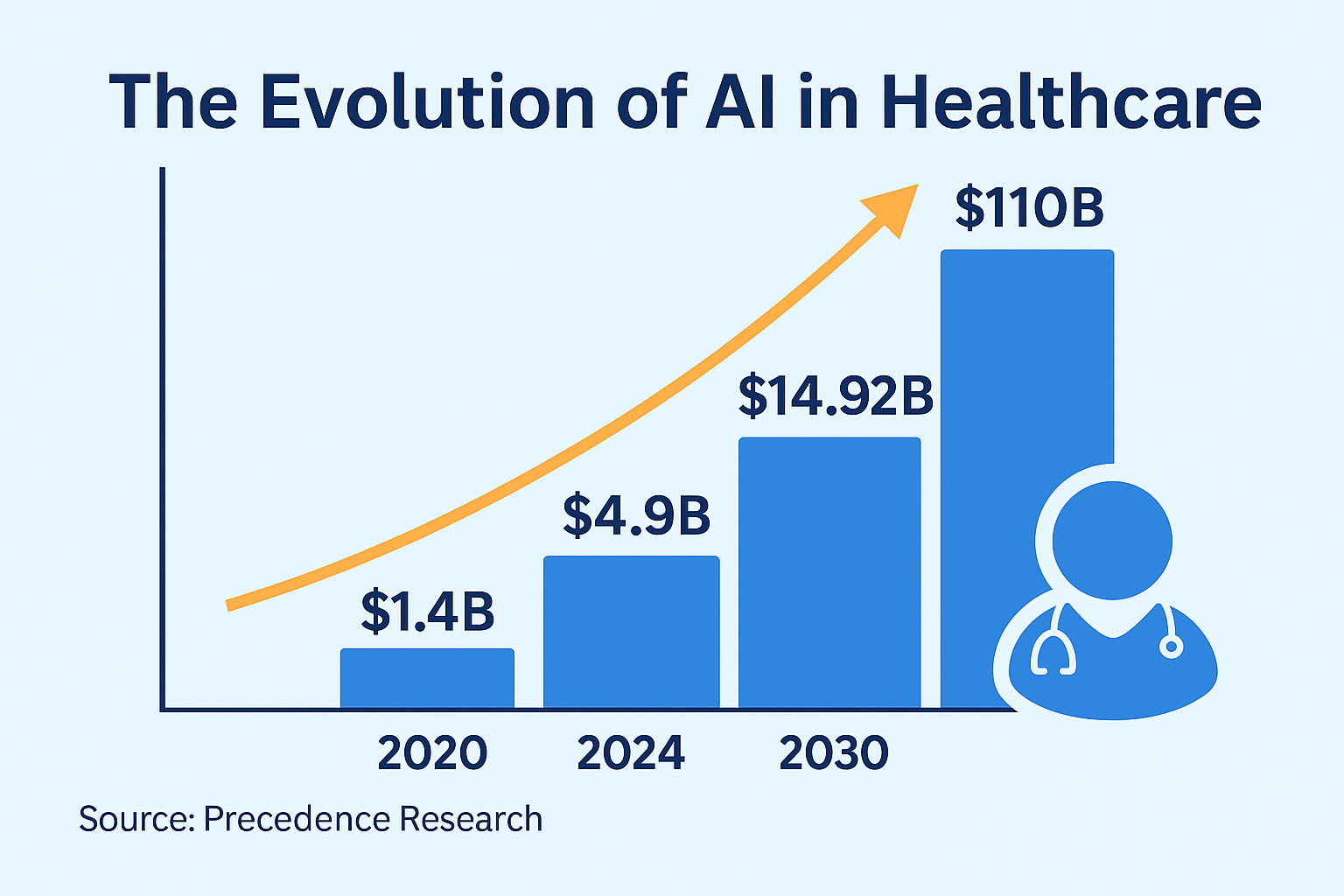
Emergency medicine has come a long way in the last few decades, but the growing patient loads and ever decreasing resources call for more effective systems. AI technologies can scan large amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions much quicker than any human might, making it especially useful in the ER.
As per a recent article in ScienceDirect, AI solutions are seeing increased used in emergency departments to improve clinical decision-making, minimize diagnostic error, and optimize patient throughput.
Improving Triage and Patient Flow
AI-Powered Triage Systems
Triaging lies at the heart of emergency medicine. AI-based triage systems can rapidly assess patients using symptoms and vital signs to predict clinical deterioration, prioritize sicker patients, and guide placement within the emergency department.
Case Example: Minimizing ED Crowding
In the US, ED overcrowding is a serious problem, especially among elderly patients. More than 130 million visits are made to U.S. emergency departments annually, and wait times have continued to increase. AI algorithms are now being used to forecast peak hours, staff levels, and delays.
According to a study by Cureus, some US hospitals have introduced AI systems that can reliably predict admitted ED patients and length of stay, thus improving overall healthcare.
Advancing Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
AI in Medical Imaging
AI’s ability to process and interpret medical images is one of its most well-known applications. Tools like Google’s DeepMind and Zebra Medical Vision use deep learning to identify anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
A ScienceDirect review concluded that AI-based systems would be able to match, or even surpass, radiologists for certain diagnoses. AI systems are currently deployed in EDs to streamline diagnoses for diseases such as stroke, intracranial hemorrhage, and lung infection.
AI-Assisted Clinical Decision Support
Apart from diagnostics, AI is also capable of providing treatment recommendations for the patient's condition, medical history, and even genomics. This type of AI-facilitated decision support is assisting ED doctors in selecting optimal therapies, dosages of drugs, and suggesting potential drug interactions in real time.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence systems are increasingly being integrated with patient monitoring equipment to present real-time data. For example, wearable biosensors can recognize changes in physiological processes and signal medical personnel regarding potential deterioration prior to it becoming evident to the naked eye.
Intracranial Hemorrhage
In a study recently published in the International Journal of Emergency Medicine, an AI-driven triage and prioritization program implemented in EDs resulted in dramatic decreases in both 30- and 120-day all-cause mortality in intracranial hemorrhage patients.
Predicting Sepsis
AI has also been useful in sepsis prediction. Early identification is critical in treating this life-threatening illness, and AI algorithms can indicate sepsis risk up to 12 hours before conventional approaches.
Automating Communication and Documentation
Reducing Administrative Burden
Clinical documentation consumes a significant portion of a physician’s time. According to several studies, emergency doctors can spend up to 50% of their shift completing documentation tasks. AI-powered scribe tools using natural language processing (NLP) can transcribe doctor-patient interactions in real-time, auto-populate forms, and even generate discharge summaries.
The Advantages of AI in Emergency Care
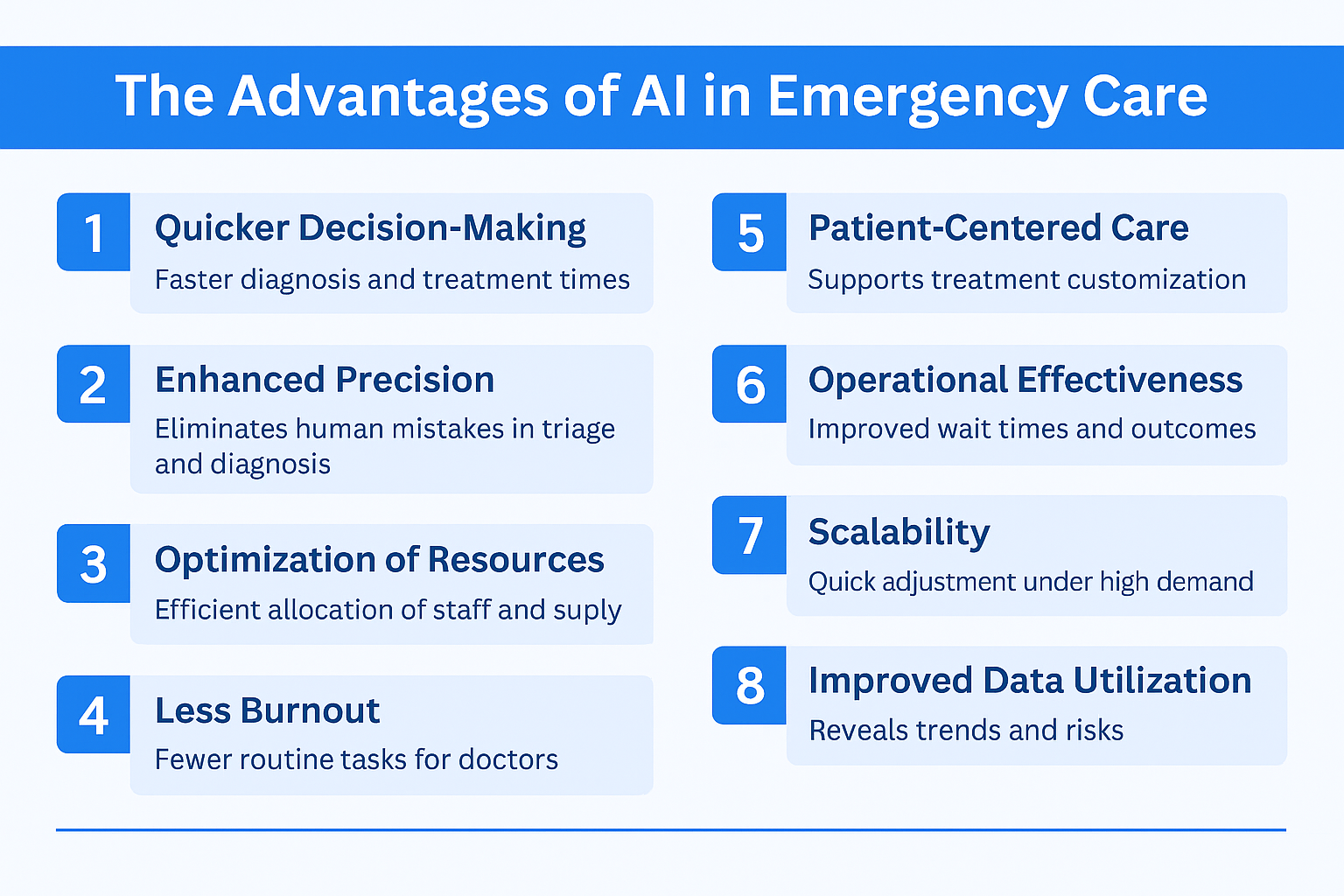
Quicker Decision-Making: AI accelerates diagnosis and treatment time considerably.
Enhanced Precision: AI improves accuracy in triage, diagnosis, and documentation.
Optimization of Resources: Predictive analytics assist hospitals in the more efficient allocation of staff and supplies.
Less Burnout: Automated routine tasks allow doctors to concentrate on patient care.
Patient-Centered Care: AI supports customized treatment plans.
Operational Effectiveness: Improved wait times and decreased hospital length of stay translate to improved ED throughput and patient outcomes.
Scalability: AI tools are able to quickly adjust under high-demand scenarios, e.g., pandemics or disasters.
Improved Training: Simulation-based AI tools assist in training new emergency staff under realistic conditions, enhancing readiness.
Enhanced Data Utilization: AI makes use of under-leveraged EHR data to reveal trends, risks, and treatment outcomes.
Improved Equity: AI can help identify care disparities and flag underrepresented populations for targeted interventions.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the advantages are numerous, several challenges remain:
Data Accuracy and Bias
AI is only as good as the data it's trained on. Incomplete, out-of-date, or biased datasets can result in inaccurate outcomes, potentially worsening health disparities. Work is being done to make training datasets more diverse and representative.
Patient Privacy
The use of AI brings concerns about the secure management of sensitive health information. HIPAA compliance is paramount. Transparency regarding how data is collected, stored, and used is critical to patient trust.
Doctor-Patient Relationship
There is a fear that excessive dependence on AI may depersonalize treatment. It is essential to preserve empathy and communication in human interaction, even as routine work is done by AI.
Liability and Accountability
Who will be liable if AI provides a wrong suggestion? Hospitals require well-defined legal guidelines and measures to reduce risk.
Technology Adoption and Training
The rate of AI technology development can exceed the capacity for effective deployment and utilization of staff. Ongoing training and transformation management are important to the successful implementation of AI.
Interoperability and Infrastructure
Most EDs continue to battle with incompatible equipment and legacy structures. AI platforms need to function smoothly with pre-existing EHRs and clinician workflows in order to make an impact.
Cost of Implementation
Steep front-end capital costs and upkeep can be prohibitive, particularly for small hospitals. However, efficiency and patient benefits could justify them in the long run.
AI in Emergency Medical Services (EMS) and Pre-Hospital Care
AI is finding its way into the business even before patients make it to the hospital. Emergency Medical Services (EMS) responders are beginning to employ AI devices for decision support, routing, and field diagnostics.
For example, AI can scan data from handheld diagnostic devices to identify stroke or cardiac arrest symptoms during transit. Real-time data transmission to the ED enables the hospital to prepare for prompt intervention upon arrival of the patient.
AI is being employed by some ambulance services in the United States for dynamic dispatching and traffic-aware routing, enhancing response times and patient outcomes.
AI’s Role in Addressing Health Disparities and Rural Emergency Care
One of the most promising aspects of AI in emergency medicine is its potential to reduce healthcare disparities, particularly in underserved and rural areas across the United States. While urban hospitals often have access to robust infrastructure and specialty care, rural EDs frequently face challenges such as staffing shortages, limited diagnostic tools, and longer patient transport times.
Closing the Rural Care Gap
Artificial intelligence solutions are closing these gaps by making remote consultations, decision support, and diagnostics possible. For example, tele-triage platforms powered by AI enable emergency clinicians in rural hospitals to work in real time with specialists in larger cities. This can be particularly useful in life-threatening cases such as trauma, stroke, or sepsis, where time is of the essence.
Mobile Diagnostics and Predictive Tools
AI-powered portable diagnostic equipment is also enhancing rural emergency care. A few U.S. health systems are outfitting ambulances with equipment using AI to interpret ECGs or identify pre-symptomatic markers for stroke. These findings are communicated to EDs before patients arrive, allowing for quicker preparation and treatment.
Enhancing Equity Through Data Insights
AI can further reveal underlying patterns within electronic health records to spot systemic care delivery disparities. Algorithms designed to flag slow treatment times or patterns of under-diagnosis within certain racial or socioeconomic populations enable EDs to initiate corrective actions that are more specific.
Policy and Funding Support
Government programs like the Rural Emergency Hospital (REH) program and Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) grants are financing the implementation of AI and telehealth in rural emergency care. These initiatives work towards making lifesaving AI technology available beyond the walls of prominent medical institutions and reach communities across the country.
Regulatory Environment and FDA Approvals
AI software applied in emergency environments should comply with strict regulatory requirements. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the U.S. has already cleared some AI-based technologies for use in radiology, sepsis risk prediction, and triage support.
FDA's Software as a Medical Device model coordinates the creation and testing of such software. Hospitals and creators also have to adhere to clinical validation requirements, which will ensure that AI software functions appropriately and safely in heterogeneous populations.
Return on Investment (ROI) and Impact on Operations
Although AI solutions are investment-heavy, they can have a significant impact on operational performance and cost reduction. By minimizing unnecessary admissions, optimizing throughput, and avoiding medical errors, AI supports financial viability.
According to a recent study, EDs with AI-based command centers achieve as much as 29% bed utilization and 37% decreases in average wait times. These benefits equate to enhanced patient satisfaction as well as improved bottom-line efficiency for hospitals.
Also, AI has the potential to lower malpractice suits by enhancing documentation accuracy and clinical decision-making support, which further enhances its ROI.
Future Trends in AI for Emergency Medicine
Looking to the future, AI will advance further in emergency medicine. Emerging trends are:
Ambient Intelligence
Intelligent sensors and AI-powered room systems that recognize patient distress without human intervention.
Generative AI for Simulation
Training software that generates realistic emergency situations for medical training.
Voice-AI for Hands-Free Documentation
Evolution of AI scribes that facilitate hands-free interaction during procedures.
Multimodal AI
Platforms that integrate imaging, lab values, and patient notes to generate comprehensive decision support.
Explainable AI
Future technologies will focus more on interpretability, allowing clinicians to comprehend and trust the decisions of AI.
AI-Driven Research
Live data synthesis by AI may assist in creating new clinical wisdom and best practices in emergency medicine.
Wearable AI Devices
Ongoing patient monitoring with wearable technology will enable remote triage and quicker intervention.
Training the Emergency Workforce to Use AI
Effective AI integration demands that healthcare providers be trained not only to operate AI tools but also to know their limitations. Residency programs and medical schools are starting to integrate AI literacy into their curricula. Simulation training programs enable emergency medicine residents to practice operating AI tools in real-life situations.
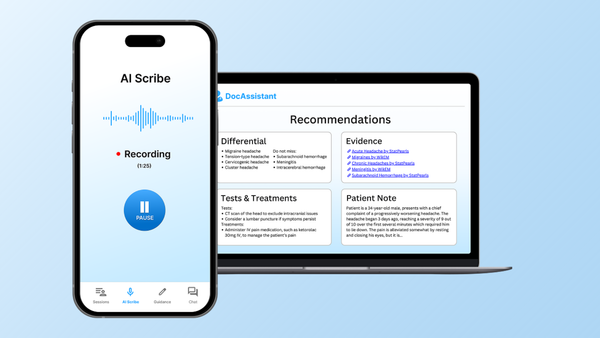
The Role of AI Scribes
Among the brightest AI solutions in emergency care are AI medical scribes. DocAssistant is one such software aimed at assisting clinicians through recording real-time dialogue and generating clinical notes automatically.
By saving documentation time, DocAssistant enables ED personnel to concentrate on providing timely and empathetic care. Integration with EHR systems provides seamless updating, and natural language capabilities ensure accuracy and context.
Conclusion
AI is bringing with it a new generation of emergency care, one that is quicker, wiser, and more responsive. From triage to treatment, real-time tracking to record-keeping, AI is augmenting all aspects of emergency medicine. However, the path to complete integration must be tread cautiously, weighing innovation against ethics, and technology against human empathy.
As AI software continues to improve and spread, emergency rooms are likely to become more responsive, precise, and empathetic. AI won't displace emergency doctors; it will empower them. By eliminating redundant work, augmenting clinical judgment, and streamlining operations, AI allows physicians to devote more time where it's needed most - at the patient's bedside. The future of emergency medicine isn’t just about speed and efficiency; it’s about delivering better care, faster, and with a human touch that technology can amplify, not replace.
About the Author
Nathan Murray, M.D. Emergency Medicine - Founder of DocAssistant
Dr. Nathan Murray is a board-certified emergency medicine physician and the founder of DocAssistant. With years of frontline clinical experience, Dr. Murray is passionate about using AI to streamline medical documentation and improve care delivery.